What is HRD?
Relationship between HR, HRR and HRD
HR (Homologous Recombination) is recombination between homologous chromosomes of non-sister chromatids or recombination that occurs within DNA molecules containing homologous sequences on the same chromosome, using unaffected chromosomes as a template to repair lost DNA sequences, and is a highly conservative process that plays a major role in DNA repair.
HRR (Homologous Recombination Repair), on the other hand, refers to the repair process performed through homologous recombination when DNA double-strand breaks occur in normal cells, which can reconnect broken DNA double-strands and maintain genomic stability, thereby ensuring the normal survival of cells.
An HRR functional abnormality resulting in its inability to repair damaged DNA is called a homologous recombination repair defect, or HRD (Homologous Recombination Deficiency).
HRR Mechanism of Action
HRR is a complex signaling pathway involving multiple steps and genes. When DNA is damaged, ATM and other recognition proteins will first identify information related to double-strand breaks, mediating damage signal transmission through BRCA1/2 and other transduction proteins. Subsequently, the effector protein RAD51 is loaded into the single-strand DNA to promote the invasion of the single strand and the formation of the Holliday junction, resulting in the completion of repair synthesis, which ultimately completes the repair of the double-strand DNA break.
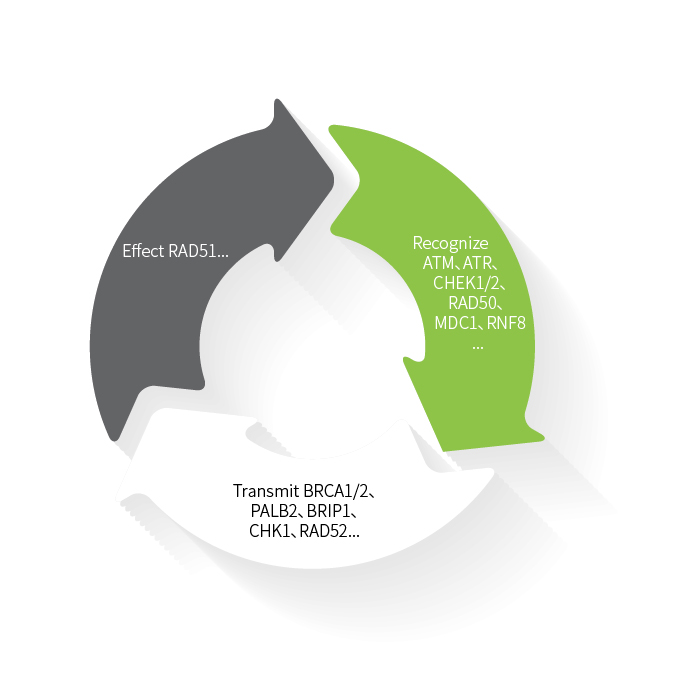
Identify ATM, ATR, CHEK1/2, RAD50, MDC1, RNF8, etc.
Effector RAD51, etc.
Transmission BRCA1/2, PALB2, BRIP1, CHK1RAD52, etc.
Figure 1 HRR Mechanism of Action
Mutations in functional genes related to the HRR pathway (HRRm) have now been demonstrated to be universal across tumors.
Clinical Role of HRD Testing
HRD produces specific, quantifiable, and stable genomic alterations, which include identifiable genetic mutations, insertion/deletion patterns, as well as chromosomal structural abnormalities, copy number variations, etc., and thereby lays the theoretical basis for the current construction of clinical testing methods for HRD. In recent years, HRD testing has been recommended in the guidelines and consensus of multiple tumor types in China [3] - [6].
Through the detection of HRD, cancer risk assessment can be performed, for example, BRCA1/2 gene mutations, which increase the risk of morbidity and mortality in a variety of tumors, including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, etc., can be detected. Additionally, because most HRD tumors show high sensitivity to PARP inhibitors (PARPi) and platinum-based drugs, the results of HRD testing can be used to predict efficacy, thereby guiding medication in clinical practice.
How HRD is Detected
Dynegene has independently developed two panels for HRR and HRD detection, both based on sample data from the Chinese population and designed with reference to the Expert Consensus on Clinical Detection and Application of Homologous Recombination Repair Defects (Version 2021). Our HRR Panel involves the coding exons of 71 genes, while our HRD Panel, which is built on the foundation established by our HRR Panel, adds more than 50,000 SNP loci and can provide customers with a comprehensive HRR/HRD detection solution, all using Dynegene's self-developed algorithm.
| Item No. |
Product Name |
Product Description |
| NY1017 |
QuarXeq HRR Probes 1.0 |
Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) Panel |
| NY1018 |
QuarXeq HRD Probes 1.0 |
Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) Panel |
Please contact us to order
 NGSHybridization Capture DNA Probe QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Tumor) QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Standard) QuarStar Liquid Pan-Cancer Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Lite Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Fusion Panel 1.0 QuarStar Pan Cancer Panel 1.0 Hybridization Capture RNA Probe QuarXeq Human All Exon Probes 3.0 HRD panel Library Preparation DNA Library Preparation Kit Fragmentation Reagent mRNA Capture Kit rRNA Depletion Kit QuarPro Superfast T4 DNA Ligase Hybridization Capture QuarHyb Super DNA Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Plus 2 Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Reagent Kit Plus QuarHyb One Reagent Kit QuarHyb Super Reagent Kit Pro Dynegene Adapter Family Dynegene Blocker Family Multiplex PCR QuarMultiple BRCA Amplicon QuarMultiple PCR Capture Kit 2.0 PathoSeq 450 Pathogen Library Corollary Reagent Streptavidin magnetic beads Equipment and Software The iQuars50 NGS Prep System
NGSHybridization Capture DNA Probe QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Tumor) QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Standard) QuarStar Liquid Pan-Cancer Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Lite Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Fusion Panel 1.0 QuarStar Pan Cancer Panel 1.0 Hybridization Capture RNA Probe QuarXeq Human All Exon Probes 3.0 HRD panel Library Preparation DNA Library Preparation Kit Fragmentation Reagent mRNA Capture Kit rRNA Depletion Kit QuarPro Superfast T4 DNA Ligase Hybridization Capture QuarHyb Super DNA Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Plus 2 Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Reagent Kit Plus QuarHyb One Reagent Kit QuarHyb Super Reagent Kit Pro Dynegene Adapter Family Dynegene Blocker Family Multiplex PCR QuarMultiple BRCA Amplicon QuarMultiple PCR Capture Kit 2.0 PathoSeq 450 Pathogen Library Corollary Reagent Streptavidin magnetic beads Equipment and Software The iQuars50 NGS Prep System Primers and Probes
Primers and Probes RNA SynthesissgRNA miRNA siRNA
RNA SynthesissgRNA miRNA siRNA



 Gene Synthesis
Gene Synthesis Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools CRISPR sgRNA Library
CRISPR sgRNA Library Antibody Library
Antibody Library Variant Library
Variant Library




 Tel: 400-017-9077
Tel: 400-017-9077 Address: Floor 2, Building 5, No. 248 Guanghua Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
Address: Floor 2, Building 5, No. 248 Guanghua Road, Minhang District, Shanghai Email:
Email: