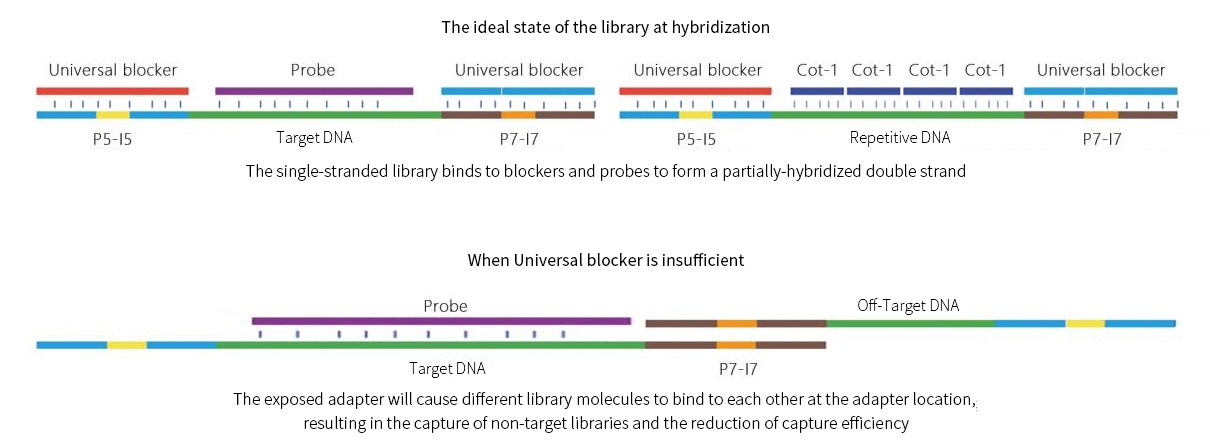
The NGS Targeted Capture Process involves using blockers for adapters to prevent the binding between adapter sequences in the library. Additionally, Cot-1 DNA is employed to block high-copy regions/low-complexity regions of library insert fragments, thereby preventing non-specific capturing of such regions caused by probe cross-hybridization.
By significantly reducing these two types of non-specific bindings, the on-target rate and data utilization can be improved. Dynegene Technology provides blocker reagents for targeted capture on both Illumina and MGI platforms. Moreover, they offer separate human Cot-1 DNA to support multiplexed hybridization, thus ensuring efficient capture for users.
Key Features
-
Excellent Blocking Performance
By blocking multiple adapter sequences and regions with a high genome copy rate or low genome sequence complexity, the non-specific binding between different library molecules is effectively reduced, and the capture efficiency is improved.
-
Versatile Applications
We offer blockers tailored for various sequencing platforms, including Illumina and MGI, and compatible with different technical processes, such as single hybridization and multiple hybridization.
-
Lower Cost
Universal blockers can be used to block multiple-hybridization libraries, and an alternative for single-hybridization can be provided, reducing the cost of each sample.
Blocking schematic
 NGSHybridization Capture DNA Probe QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Tumor) QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Standard) QuarStar Liquid Pan-Cancer Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Lite Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Fusion Panel 1.0 QuarStar Pan Cancer Panel 1.0 Hybridization Capture RNA Probe QuarXeq Human All Exon Probes 3.0 HRD panel Library Preparation DNA Library Preparation Kit Fragmentation Reagent mRNA Capture Kit rRNA Depletion Kit QuarPro Superfast T4 DNA Ligase Hybridization Capture QuarHyb Super DNA Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Plus 2 Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Reagent Kit Plus QuarHyb One Reagent Kit QuarHyb Super Reagent Kit Pro Dynegene Adapter Family Dynegene Blocker Family Multiplex PCR QuarMultiple BRCA Amplicon QuarMultiple PCR Capture Kit 2.0 PathoSeq 450 Pathogen Library Corollary Reagent Streptavidin magnetic beads Equipment and Software The iQuars50 NGS Prep System
NGSHybridization Capture DNA Probe QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Tumor) QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Standard) QuarStar Liquid Pan-Cancer Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Lite Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Fusion Panel 1.0 QuarStar Pan Cancer Panel 1.0 Hybridization Capture RNA Probe QuarXeq Human All Exon Probes 3.0 HRD panel Library Preparation DNA Library Preparation Kit Fragmentation Reagent mRNA Capture Kit rRNA Depletion Kit QuarPro Superfast T4 DNA Ligase Hybridization Capture QuarHyb Super DNA Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Plus 2 Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Reagent Kit Plus QuarHyb One Reagent Kit QuarHyb Super Reagent Kit Pro Dynegene Adapter Family Dynegene Blocker Family Multiplex PCR QuarMultiple BRCA Amplicon QuarMultiple PCR Capture Kit 2.0 PathoSeq 450 Pathogen Library Corollary Reagent Streptavidin magnetic beads Equipment and Software The iQuars50 NGS Prep System Primers and Probes
Primers and Probes RNA SynthesissgRNA miRNA siRNA
RNA SynthesissgRNA miRNA siRNA



 Gene Synthesis
Gene Synthesis Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools CRISPR sgRNA Library
CRISPR sgRNA Library Antibody Library
Antibody Library Variant Library
Variant Library





 Tel: 400-017-9077
Tel: 400-017-9077 Address: Floor 2, Building 5, No. 248 Guanghua Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
Address: Floor 2, Building 5, No. 248 Guanghua Road, Minhang District, Shanghai Email:
Email: