Nucleic acid synthesis stands as a crucial technology supporting advancements in life sciences and applied research. Driven by the demands of biomedicine, genomics, synthetic biology, and beyond, ultra-high-throughput nucleic acid synthesis holds extensive application value and numerous potential scenarios.
Dynegene, as a pioneer in next-generation nucleic acid synthesis in China, has shattered the constraints of existing technologies. We have successfully developed the DYHOW platform, a next-generation ultra-high-throughput DNA synthesis platform with complete proprietary intellectual property, which enables synthesizing commercialized nucleic acid. The latest DYHOW-3B platform significantly enhances DNA synthesis throughput, reduces synthesis costs, offers a maximum length of 350 nt with 4.35 million different custom sequences available for customers, and ensures high accuracy and uniformity. This platform propels the rapid development of synthetic biology-related fields, addressing research and production challenges in medicine, food, agriculture, and more.
Highlights
-
High throughput
A throughput of up to 4.35million custom oligos on one single chip
Up to 350 nt in length
-
High Quality
High uniformity and the coverage rate of >99%
Average error Rate: Approximately 1/1500
-
No re-used Chip
Avoid cross-contamination
Batch-to-batch stability
Turnaround Time
| Service Type |
TAT |
Notes |
|
Standard
|
≤150nt: 1 week
151-230nt: 2 weeks
231-350nt: 3 weeks
|
lf advanced purification (PAGE) is required, the TAT would be extended with an additional 2 days.
lf the throughput exceeds 1.08 million, the TAT might vary.
|
|
Priority
|
For oligo pool between120k to 1,080k with 2-120 nt in length, TAT could be as fast as 1 working day!
(Order today, shipped tomorrow!)
|
Priority Service operates on a reservation basis and requires prior communication to be achieved.
If you places stable, recurring orders for pools of consistent length and scale, even if the orders don't meet the Priority Service criteria, the delivery cycle is expected to be shorter than standard delivery, approaching the expedited timeline of Priority Service.
|
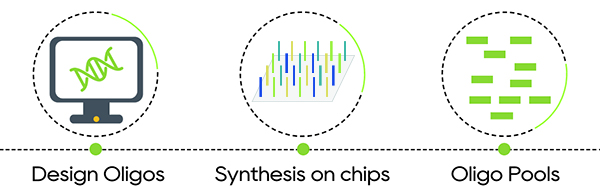
Workflow
Applications
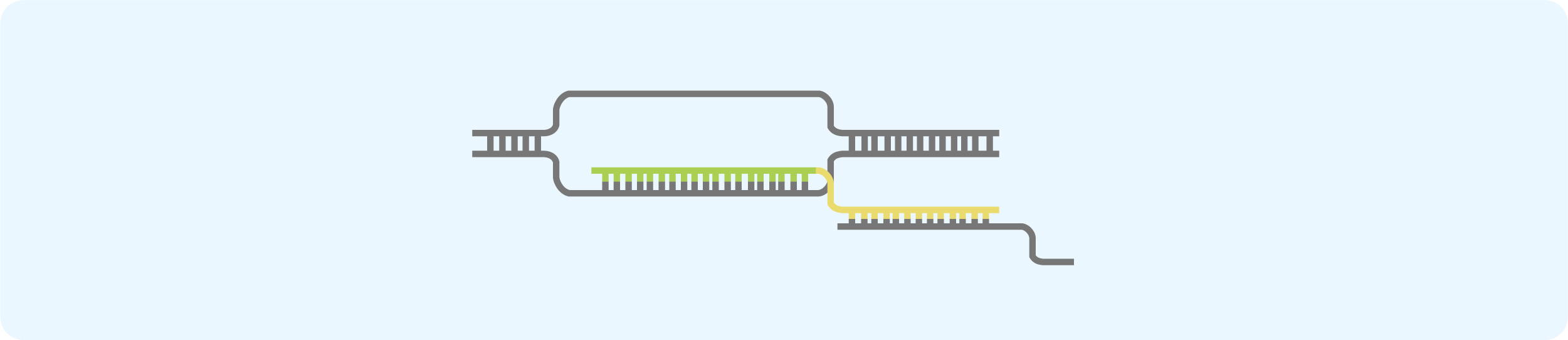
● CRISPR sgRNA Library
sgRNA library construction - consists of thousands of plasmids containing multiple sgRNAs for each target gene. These libraries leverage the efficiency and specificity of the CRISPR gene editing technology to either knock out gene expression or transcriptionally activate genes in the genome. It is particularly valuable for conducting high-throughput screening of important molecular targets.

● Variant Library
Variant libraries are instrumental in synthesizing thousands of gene variants simultaneously, allowing for the identification of key structural and functional sites. These libraries play a prominent role in diverse fields, such as protein engineering, metabolic engineering, and antibody optimization.
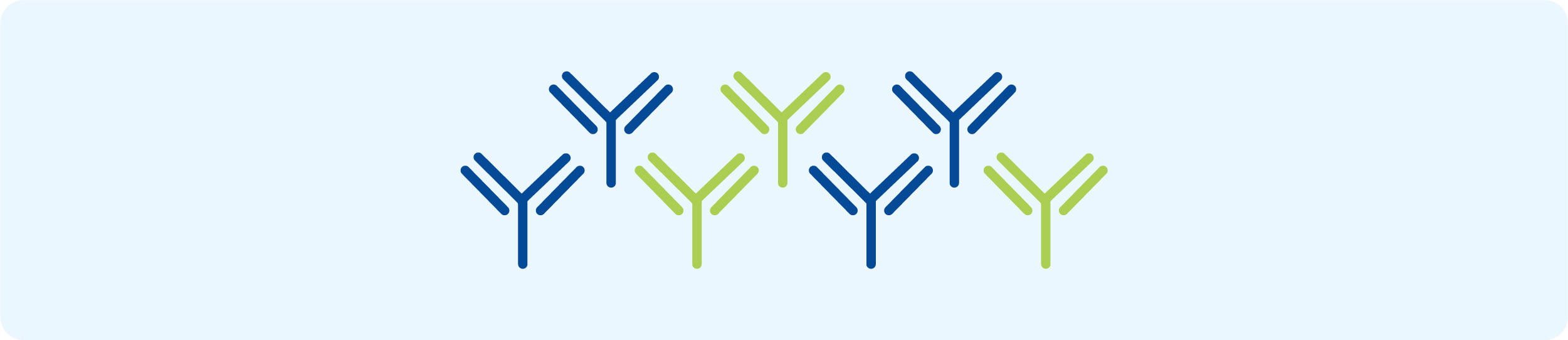

● Antibody Library
Synthetic antibody libraries are constructed from scratch using designed synthetic DNA, allowing for the creation of specific antibodies targeted against a wide range of protein antigens. Antibody libraries streamline the creation of specific antibodies derived from natural immunization, serving as strong tools to accelerate the antibody discovery process. This not only simplifies the process but also enhances the efficiency and precision, catalyzing breakthroughs in antibody research.
● Massively Parallel Reporter Assays (MPRA)
The massively parallel reporter assay (MPRA) facilitates the simultaneous functional validation of thousands of regulatory elements through the utilization of high-throughput sequencing and barcode technology. This approach aids researchers in unraveling the functional implications of genetic variation and identifying genetic variants linked to human diseases and traits.

● Targeted Sequencing
Target regions can be efficiently enriched for sequencing by synthesizing specific probes on a high-throughput synthesis platform, resulting in reduced sequencing costs.
● Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Oligo pools can be utilized to expedite the development of FISH probes and aid in spatial transcriptome research. For instance, MerFish can identify and analyze gene expression profiles that are spatially localized in individual cells.

● High-throughput Gene Synthesis
The field of synthetic biology is experiencing rapid growth, which has led to an enormous demand for synthetic genes that traditional gene synthesis capabilities cannot keep up with. Fortunately, high throughput oligo synthesis provides the capacity to synthesize massive amounts of genes simultaneously.

● DNA Storage
DNA sequences emerge as a promising medium for data storage, boasting unparalleled attributes, including remarkable density, stability, and durability. Positioned as an alternative to address the challenges of data storage insufficiency, DNA storage holds immense potential to revolutionize the field with its futuristic capabilities.
 NGSHybridization Capture DNA Probe QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Tumor) QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Standard) QuarStar Liquid Pan-Cancer Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Lite Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Fusion Panel 1.0 QuarStar Pan Cancer Panel 1.0 Hybridization Capture RNA Probe QuarXeq Human All Exon Probes 3.0 HRD panel Library Preparation DNA Library Preparation Kit Fragmentation Reagent mRNA Capture Kit rRNA Depletion Kit QuarPro Superfast T4 DNA Ligase Hybridization Capture QuarHyb Super DNA Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Plus 2 Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Reagent Kit Plus QuarHyb One Reagent Kit QuarHyb Super Reagent Kit Pro Dynegene Adapter Family Dynegene Blocker Family Multiplex PCR QuarMultiple BRCA Amplicon QuarMultiple PCR Capture Kit 2.0 PathoSeq 450 Pathogen Library Corollary Reagent Streptavidin magnetic beads Equipment and Software The iQuars50 NGS Prep System
NGSHybridization Capture DNA Probe QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Tumor) QuarStar Human All Exon Probes 4.0 (Standard) QuarStar Liquid Pan-Cancer Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Lite Panel 3.0 QuarStar Pan-Cancer Fusion Panel 1.0 QuarStar Pan Cancer Panel 1.0 Hybridization Capture RNA Probe QuarXeq Human All Exon Probes 3.0 HRD panel Library Preparation DNA Library Preparation Kit Fragmentation Reagent mRNA Capture Kit rRNA Depletion Kit QuarPro Superfast T4 DNA Ligase Hybridization Capture QuarHyb Super DNA Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Plus 2 Reagent Kit QuarHyb DNA Reagent Kit Plus QuarHyb One Reagent Kit QuarHyb Super Reagent Kit Pro Dynegene Adapter Family Dynegene Blocker Family Multiplex PCR QuarMultiple BRCA Amplicon QuarMultiple PCR Capture Kit 2.0 PathoSeq 450 Pathogen Library Corollary Reagent Streptavidin magnetic beads Equipment and Software The iQuars50 NGS Prep System Primers and Probes
Primers and Probes RNA SynthesissgRNA miRNA siRNA
RNA SynthesissgRNA miRNA siRNA



 Gene Synthesis
Gene Synthesis Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools CRISPR sgRNA Library
CRISPR sgRNA Library Antibody Library
Antibody Library Variant Library
Variant Library













 Tel: 400-017-9077
Tel: 400-017-9077 Address: Floor 2, Building 5, No. 248 Guanghua Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
Address: Floor 2, Building 5, No. 248 Guanghua Road, Minhang District, Shanghai Email:
Email: